Introduction
The focal point of this project is the modeling of the mechanical system of a jack bouncing around in the boundary of a box.
Overall System and Reference Frames
Attached is a detailed drawing of the system, illustrating all the frames in use, complete with frame labels. These frames and their labels have been consistently used and identified in the code to maintain clarity and coherence.
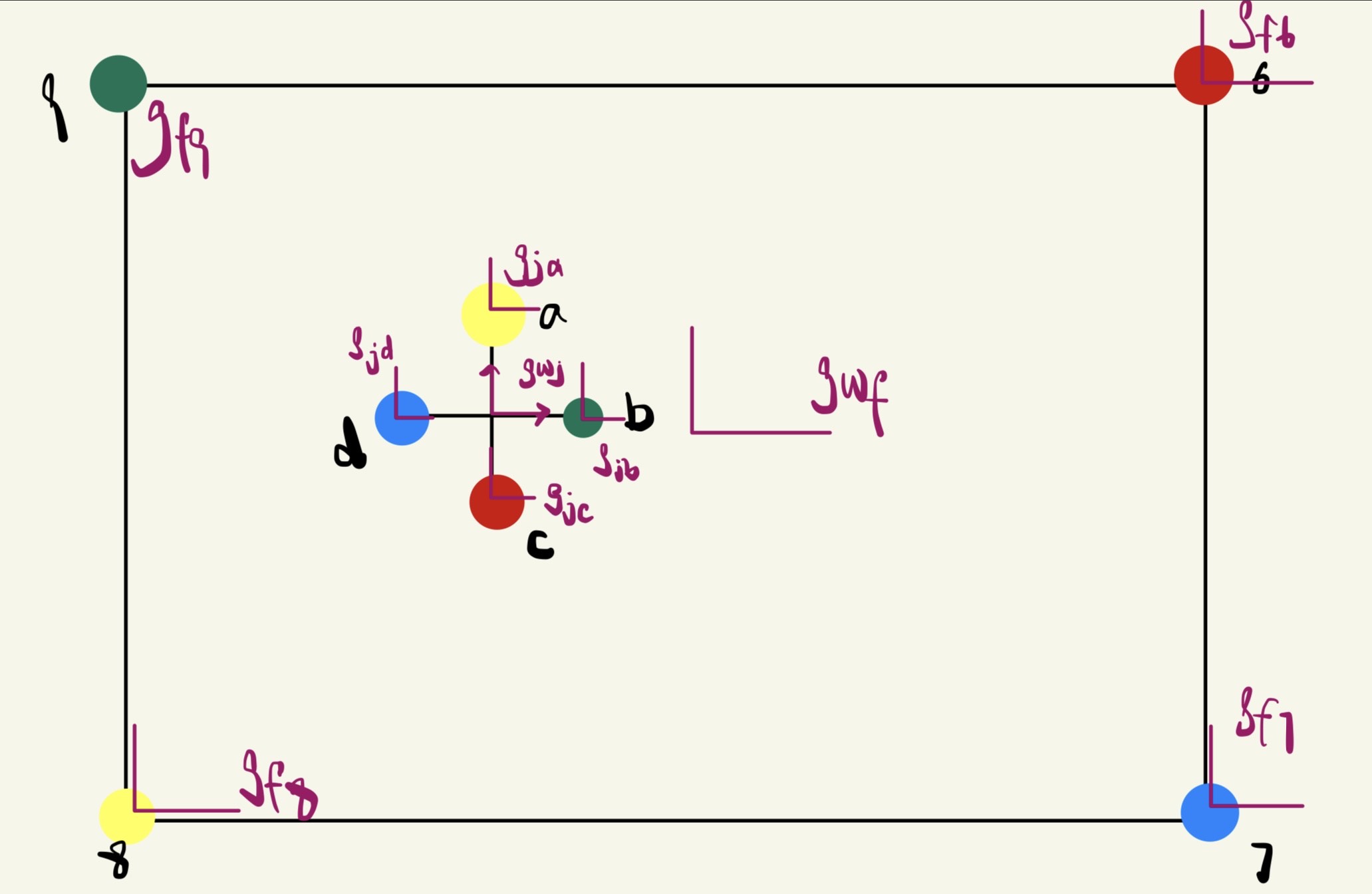
Frames
The base frame for the box is called g_wf, where f is the center of the box. g_f6, g_f7, g_f8, g_f9 are the relative frames based on the box center. The frame between world and box vertices can be generated through cross product of g_wf and g_f6, g_f7, g_f8, g_f9.
The base frame for the jack is called g_wj, where j is the center of the jack. g_jb, g_ja, g_jc, g_jd are the relative frames based on the box center. The frame between world and box vertices can be generated through cross product of g_wj and g_jb, g_ja, g_jc, g_jd.
Euler-Lagrange equations
The Euler Lagrange equation is calculated based on the:
- Calculate Lagrangian equation by
L = KE - V, whereKEis kinetic energy of both jack and box andVis the potential energy of both jack and box. The python script calculating the kinetic energyKEand potential energyVis shown below:
#Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
#frame kinetic energy
KE_frame = sym.simplify(0.5*(v_wf).T*Inertia_frame_mat*v_wf)
#jack kinetic energy
KE_vwa = sym.simplify(0.5*(v_wa).T*Inertia_jack_mat*v_wa)
KE_vwb = sym.simplify(0.5*(v_wb).T*Inertia_jack_mat*v_wb)
KE_vwc = sym.simplify(0.5*(v_wc).T*Inertia_jack_mat*v_wc)
KE_vwd = sym.simplify(0.5*(v_wd).T*Inertia_jack_mat*v_wd)
KE_jack = sym.simplify(KE_vwa + KE_vwb + KE_vwc + KE_vwd)
KE_total = sym.simplify(KE_jack+ KE_frame)
hf = sym.simplify(sym.Matrix([g_wf[1,3]]))
h_wa = sym.simplify(sym.Matrix([g_wa[1,3]]))
h_wb = sym.simplify(sym.Matrix([g_wb[1,3]]))
h_wc = sym.simplify(sym.Matrix([g_wc[1,3]]))
h_wd = sym.simplify(sym.Matrix([g_wd[1,3]]))
V_f = Mf*gravity*hf[0]
V_wa = m_j_point*gravity*h_wa[0]
V_wb = m_j_point*gravity*h_wb[0]
V_wc = m_j_point*gravity*h_wc[0]
V_wd = m_j_point*gravity*h_wd[0]
V_total = sym.simplify(sym.Matrix([V_f + V_wa + V_wb + V_wc + V_wd]))
- Define symtem variables as
q = [x_f, y_f, theta_f, x_j, y_j, theta_j]and useLagrangian Equationandqto calculateEuler Lagrangian equation.
Add the Constraints to the system
To add the constraints to the system, constraints will be found through the area A between the vertex of the jack and the side of the box. The area could be found through the cross product of two vectors on side of the box and the jack vertex.
Once the jack and the box collide, the area A should be 0. However, considering the movement tolerance, I set up a very small threshold for that.
Update the external forces
External forces are defined by a force matrix corresponding to the variables in q. I defined a torque of 30 N-m on the box and an upward force on the box to hold the box from falling down. The force matrix is Force_Matrix = symMatrix([0, Force, 30, 0, 0, jack_torque]).
Note, the jack_torque = 0 since they are point mass.
Apply the impact update laws
Impact update function can be found at cell 13 of 19 where it takes a current state variable and an index of phi, constraint. Then it will utilize the following function to do the impact update.